Home » Keywords: » Geometric Dimensioning and Tolerancing (GD&T)
Items Tagged with 'Geometric Dimensioning and Tolerancing (GD&T)'
ARTICLES
Measurement
Metrology and Microscopy for Electronics Quality Assurance — in One Machine?
Compliance can often only be achieved through both metrology and microscopy tools.
March 5, 2024
Quality 101
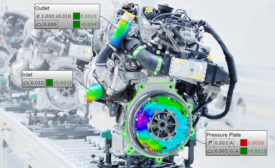
GD&T for Electric Vehicles Supports Consistent Quality Control
GD&T allows engineers to define feature relationships, ensuring proper alignment and interchangeability.
October 17, 2023
Aerospace | NDT in Aerospace
How Advancing CT Analysis Capabilities Support Collaboration and Product Quality
The looping of CT analysis via digital models can improve every aspect of the design-to-production cycle.
July 10, 2023
Quality Headline
NIMS Offers Innovative Teaching Technique to Make GDT a “Native Tongue”
June 13, 2022
What Is a Digital Twin?
Digital twin technology helps organizations to use real-time data, mockups, algorithms, and AI to create a virtual depiction of a physical object, process, or service.
May 9, 2022
Measurement
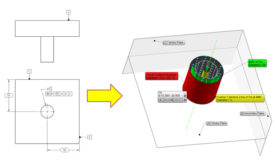
Geometric Dimensioning and Tolerancing
Let's review some of the elements of geometric dimensioning and tolerancing.
April 1, 2022
Sponsored Content
Why Knowing GD&T Inside Out is Essential in Machining Today
March 22, 2022
Sponsored Content
GD&T for Beginners: MMC & Bonus Tolerance, Explained in 3D
March 22, 2022
From the Editor | Darryl Seland
Indecision: From Aristotle and Buridan to Metastability and Digital Circuits.
February 8, 2022
Get our new eMagazine delivered to your inbox every month.
Stay in the know with Quality’s comprehensive coverage of the manufacturing and metrology industries.
SUBSCRIBE TODAY!Copyright ©2024. All Rights Reserved BNP Media.
Design, CMS, Hosting & Web Development :: ePublishing